HashSet 是一个优化过的无序集合,提供对元素的高速查找和高性能的set集合操作,而且 HashSet 是在 .NET 3.5 中被引入的,在 System.Collection.Generic 命名空间下,这篇就来讨论一下如何使用这个 HashSet。
要运行本篇文章的案例代码,你需要安装一下 Visual Studio 2019,如果没有的话可以到官网下载一下。
使用 VS 创建一个 .NET Core 控制台程序
首先,我通过 VS2019 创建一个 .NET Core 控制台程序,创建可以参考下面步骤:
- 打开 Visual Studio IDE
- 点击创建
Create new project - 在
Create new project窗口上,从模板列表中选择:Console App (.NET Core) - 点击下一步
- 在
Configure your new project界面填好你的项目名称和存放路径
这样我们就创建好了一个新项目,本文的后面部分就会在这个项目里来给大家分享 HashSet 的一些必备知识。
HashSet 到底是什么
所谓的HashSet,指的就是 System.Collections.Generic 命名空间下的 HashSet<T> 类,它是一个高性能,无序的集合,因此HashSet它并不能做排序操作,也不能包含任何重复的元素,Hashset 也不能像数组那样使用索引,所以在 HashSet 上你无法使用 for 循环,只能使用 foreach 进行迭代,HashSet 通常用在处理元素的唯一性上有着超高的性能。
HashSet<T> 实现了如下几个接口:
public class HashSet<T> : System.Collections.Generic.ICollection<T>,
System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<T>,
System.Collections.Generic.IReadOnlyCollection<T>,
System.Collections.Generic.ISet<T>,
System.Runtime.Serialization.IDeserializationCallback,
System.Runtime.Serialization.ISerializable
{
}
HashSet 只能包含唯一的元素,它的内部结构也为此做了专门的优化,值得注意的是,HashSet 也可以存放单个的 null 值,可以得出这么一个结论:如何你想拥有一个具有唯一值的集合,那么 HashSet 就是你最好的选择,何况它还具有超高的检索性能。
从 HashSet 中查找一个元素
如果想判断某一个元素是否在 HashSet 内,建议使用 Contains 进行判断,代码如下:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
HashSet<string> hashSet = new HashSet<string>();
hashSet.Add("A");
hashSet.Add("B");
hashSet.Add("C");
hashSet.Add("D");
if (hashSet.Contains("D"))
Console.WriteLine("The required element is available.");
else
Console.WriteLine("The required element isn’t available.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
HashSet中的元素唯一性
如果你向 HashSet 中插入重复的元素,它的内部会忽视这次操作而不像别的集合一样抛出异常,接下来展示一下代码:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
HashSet<string> hashSet = new HashSet<string>();
hashSet.Add("A");
hashSet.Add("B");
hashSet.Add("C");
hashSet.Add("D");
hashSet.Add("D");
Console.WriteLine("The number of elements is: {0}", hashSet.Count);
Console.ReadKey();
}
当你执行了这个程序,输出结果如下图:

现在可以考虑一下下面的代码段,它展示了重复的元素是如何被剔除的。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] cities = new string[] {
"Delhi",
"Kolkata",
"New York",
"London",
"Tokyo",
"Washington",
"Tokyo"
};
HashSet<string> hashSet = new HashSet<string>(cities);
foreach (var city in hashSet)
{
Console.WriteLine(city);
}
}
当你执行完上面的程序,重复的城市名称已经被移除了。

从 HashSet 中移除元素
从HashSet 中删除某一个元素可以调用 Remove 方法,它的语法结构如下:
public bool Remove (T item);
如果在集合中找到了这个元素,Remove方法将会删除这个元素并且返回true,否则返回 false。
下面的代码片段展示了如何使用 Remove 方法删除 HashSet 中的元素
string item = "D";
if(hashSet.Contains(item))
{
hashSet.Remove(item);
}
如果你想删除 HashSet 中的所有元素,可以调用 Clear 方法。
HashSet 的 set操作
HashSet提供了非常多的方法用于 set集合 操作上,比如说:IntersectWith, UnionWith, IsProperSubsetOf, ExceptWith, 和 SymmetricExceptWith
IsProperSubsetOf
这个 IsProperSubsetOf 用于判断 HashSet 是否为某一个集合的完全子集,可以看下面的例子:
HashSet<string> setA = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "B", "C", "D" };
HashSet<string> setB = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "B", "C", "X" };
HashSet<string> setC = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "B", "C", "D", "E" };
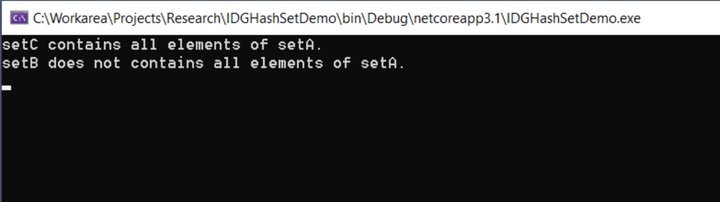
if (setA.IsProperSubsetOf(setC))
Console.WriteLine("setC contains all elements of setA.");
if (!setA.IsProperSubsetOf(setB))
Console.WriteLine("setB does not contains all elements of setA.");
如果你执行了上面这个程序,你会在控制台上看到如下的输出:
UnionWith
UnionWith方法常用于集合的合并,比如说下面的代码:
HashSet<string> setA = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "B", "C", "D", "E" };
HashSet<string> setB = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "B", "C", "X", "Y" };
setA.UnionWith(setB);
foreach(string str in setA)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
当你执行完上面的代码,SetB 集合会被 SetA 集合吞掉,最后 SetA 集合将会是包括:"A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "X", and "Y" 。
IntersectWith
IntersectWith 方法常用于表示两个 HashSet 的交集,下面的例子或许会让你更加理解:
HashSet<string> setA = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "B", "C", "D", "E" };
HashSet<string> setB = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "X", "C", "Y"};
setA.IntersectWith(setB);
foreach (string str in setA)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
当你运行了上面的这段程序,只有两个 HashSet 中都存在的元素才会输出到控制台中,输出结果如下所示:

ExceptWith
ExceptWith 方法表示数学上的减法操作,这个时间复杂度是 O(N),假定你有两个HashSet 集合,分别叫 setA 和 setB,并且用了下面的语句。
setA.ExceptWith(setB);
它返回的元素为: setA中有,setB中没有 的最终结果,如果还不明白的话,使用如下代码辅助理解:
HashSet<string> setA = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "B", "C", "D", "E" };
HashSet<string> setB = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "X", "C", "Y" };
setA.ExceptWith(setB);
foreach (string str in setA)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
当你执行了上面这段程序,元素 B,D,E 将会输出到控制台上。

SymmetricExceptWith
SymmetricExceptWith 方法常用于修改一个 HashSet 来存放两个 HashSet 都是唯一的元素,换句话说,我要的就是两个集合都不全有的元素,如果还不明白的话,考虑下面的代码段:
HashSet<string> setA = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "B", "C", "D", "E" };
HashSet<string> setB = new HashSet<string>() { "A", "X", "C", "Y" };
setA.SymmetricExceptWith(setB);
foreach (string str in setA)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
当你执行完上面的代码,你会发现,setA中有而setB中没有 和 setB中有而setA中没有的元素将会输出到控制台中。

我们知道数组的平均复杂度是 O(N),这里的 n 表示数组里的元素数量,而访问 HashSet 中的某一个元素,它的复杂度为 O(1),这个常量复杂度就决定了 HashSet 在快速检索 和执行 set集合 操作上是一个非常好的选择,你也可以使用 List 去存储某些有指定顺序的元素,同时也可以包含重复的值。